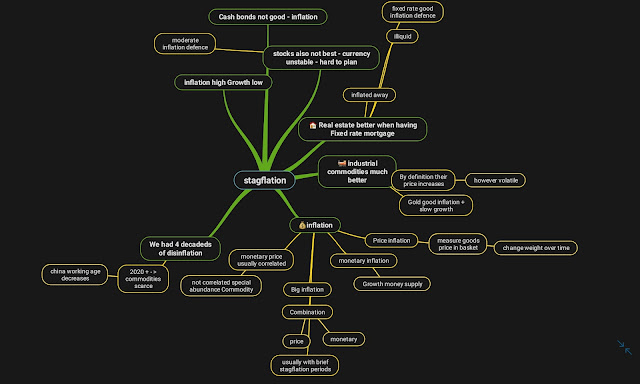
What is stagflation? Stagflation is an economic state where we have both below economical states happening simultaneously, inflation and no growth. We can have periods of inflation, we can have periods of no growth, but when we have them together, we call this stagflation.
So, stagflation is when we have both:
- We have inflation
- We don't have growth
Let's define inflation, we have two mainstream definitions:
- Price inflation – the prices are getting higher
- We have a measure of a few goods in a basket – warning which goods
- The weight of these goods in this index changes over time to reflect their real life ratio
- Monetary inflation – increase in money supply
- Usually increase in money supply should reflect the actual economic growth
We actually see big inflation in a combination of both price inflation and also monetary inflation. During inflation periods, we have brief stagflation periods.
Presently, we have over 4 decades of disinflation, but since 2020+ we started having commodities scarce and combining this with the monetary inflation we now have inflation that could start a new period.

What to invest during stagflation:
- Bonds – not good relative fixed yields
- Stocks – Medium they rise, but they have issues planning for future due to instability in currency
- Real estate – better but not liquid
- Industrial Commodities – best could be unstable at first – part of definition of inflation rise in prices of commodities.
To summarize, good investment during stagflation
- Cash and bonds do not give us any protection from inflation very minor
- Stocks are only moderate inflation defense
- Anything with fixed rate yield like bonds is not good
- Commodities while volatile, while good, can also be volatile in prices
- The industrial commodities are much better like oil, nickle, uranium
- Gold is also good during inflation and slow growth – during stagflation
The current best book to understand the global economic state

Comments
Post a Comment